About this clinic
Diabetic retinopathy(DR)is one of the leading causes of adult blindness worldwide, together with an increased rate of the patients having diabetes mellitus (DM). DR is the second most common cause of blindness in Japan, next to glaucoma1).
This outpatient clinic provides the accurate diagnosis using various imaging modalities and the advanced treatment of DR by retinal specialists.
What is DR?
Retinal microvasculature is specifically affected in DR, and the fundus shows characteristic features. One of the grading systems of diabetic retinopathy is as follows. The therapeutic strategies are different in each stage, and variable in each patient.
1.Simple diabetic retinopathy (SDR)
Microvascular injury by high blood glucose level results in multiple microaneurysms (MA) or intra-retinal dot/blot hemorrhages from damaged microvessels. Hard yellowish exudates or retinal edema, derived from aneurysmal leakage, are frequently found in the retina.
Even in this early stage, the diabetic macular edema (DME) occurs and impairs the central vision. The treatment for DME is necessary when clinically significant macula edema is found.
2.Pre-proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PPDR)
Progressive microvascular damage leads to loss of microvascular capillary network (non perfusion area: NPA) at this stage. Cotton-wool like exudates reflecting retinal ischemia are frequently found in this stage, as well as increased amount of retinal hemorrhages. In the eyes with NPA shown by fluorescein angiography (FA), focal laser photocoagulation onto retinal NPA is considered to prevent further progression. Treatments for macular edema are required in more cases than earlier stage.
3.Proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR)
As a result of vast ischemic changes of retinal vessels, new vessels (NV) on retina vessels or optic disc develop. NV is abnormal, fragile vessels, resulting in severe hemorrhage to vitreous cavity. Additionally, NV forms fibrovascular membrane, which cause tractional retinal detachment. Significant vision loss is not rare due to these severe complications. Pan retinal laser photocoagulation (PRP) is required following evaluation of ischemia by FA. Surgical treatment?vitrectomy is often required for anatomical repair of retinal detachment or removal of vitreous hemorrhage. DME is still troublesome complication in this stage.
What is DME?
DME is found in any stage of DR. The causes of diabetic macular edema are leakage from microaneurysm, damaged vessels or RPE dysfunction. As macula is critical area for vision, DME is the most frequent cause of visual impairment in DR.
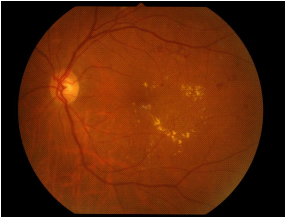
How we assess and treat DR/DME.
Our strategy to treat DR starts from appropriate evaluation and diagnosis.
In addition to routine examination including visual acuity examination, ophthalmoscopic evaluation or intraocular pressure measurements etc, FA or optical coherent tomography (OCT) are performed to assess retinal ischemic change or edema.
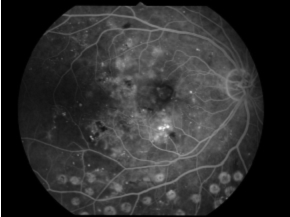
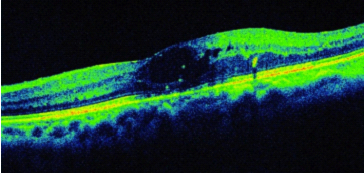
In case of retinal ischemia, laser photocoagulation is indicated.
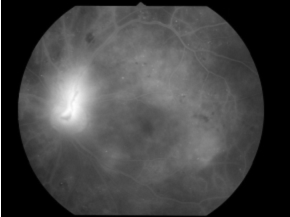
Variable therapeutical tools are recently available for DME treatment. In addition to conventional direct/grid laser therapy, administrations of anti-VEGF drug (Ranibizumab) or steroid (Triamcinolone acetonide) are effective in many cases. Surgical treatment (vitrectomy) is another choice of the diabetic retinal complication. We try to perform the most proper therapy for each patient, using the most advanced imaging modalities and treatment options. In the near future, we have a plan to introduce sub-threshold photocoagulation to macular edema-one of the latest management of DME.
Opening hours
14:30-16:00 Thursday
Booking is required.
1)Report from Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare Japan, 2005
